WordPress is the most popular open-source blogging system and CMS on the Web. It is based on PHP and MySQL. Its features can be extended with thousands of free plugins and themes.
In this tutorial we will install WordPress on Apache2 server .
This is assuming that you have an Ubuntu Server already running.
Install Dependencies
To install PHP and Apache, use following command:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install apache2 \
ghostscript \
libapache2-mod-php \
mysql-server \
php \
php-bcmath \
php-curl \
php-imagick \
php-intl \
php-json \
php-mbstring \
php-mysql \
php-xml \
php-zipInstall WordPress
We will use the release from WordPress.org rather than the APT package in the Ubuntu Archive, because this is the preferred method from upstream WordPress. This will also have fewer “gotcha” problems that the WordPress support volunteers will not be able to anticipate and therefore be unable to help with.
Create the installation directory and download the file from WordPress.org:
sudo mkdir -p /srv/www
sudo chown www-data: /srv/www
curl https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz | sudo -u www-data tar zx -C /srv/www
Note that this sets the ownership to the user
www-data, which is potentially insecure, such as when your server hosts multiple sites with different maintainers. You should investigate using a user per website in such scenarios and make the files readable and writable to only those users. This will require configuring PHP-FPM to launch a separate instance per site each running as the site’s user account. In such setup thewp-config.phpshould (read: if you do it differently you need a good reason) be readonly to the site owner and group and other permissions set to no-access (chmod 400). This is beyond the scope of this guide, however.
Configure Apache for WordPress
Create Apache site for WordPress. Create /etc/apache2/sites-available/wordpress.conf with following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot /srv/www/wordpress
<Directory /srv/www/wordpress>
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride Limit Options FileInfo
DirectoryIndex index.php
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory /srv/www/wordpress/wp-content>
Options FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Enable the site with:
sudo a2ensite wordpress
Enable URL rewriting with:
sudo a2enmod rewrite
Disable the default “It Works” site with:
sudo a2dissite 000-default
Or, instead of disabling the “it works” page, you may edit our configuration file to add a hostname that the WordPress installation will respond to requests for. This hostname must be mapped to your box somehow, e.g. via DNS, or edits to the client systems’ /etc/hosts file (on Windows the equivalent is C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts). Add ServerName as below:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName hostname.example.com
... # the rest of the VHost configuration
</VirtualHost>
Finally, reload apache2 to apply all these changes:
sudo service apache2 reloadConfigure database
To configure WordPress, we need to create MySQL database. Let’s do it!
$ sudo mysql -u root
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 7
Server version: 5.7.20-0ubuntu0.16.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE wordpress;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0,00 sec)
mysql> CREATE USER wordpress@localhost IDENTIFIED BY '<your-password>';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0,00 sec)
mysql> GRANT SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,CREATE,DROP,ALTER
-> ON wordpress.*
-> TO wordpress@localhost;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0,00 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0,00 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
Enable MySQL with sudo service mysql start.
Configure WordPress to connect to the database
Now, let’s configure WordPress to use this database. First, copy the sample configuration file to wp-config.php:
sudo -u www-data cp /srv/www/wordpress/wp-config-sample.php /srv/www/wordpress/wp-config.php
Next, set the database credentials in the configuration file (do not replace database_name_here or username_here in the commands below. Do replace <your-password> with your database password.):
sudo -u www-data sed -i 's/database_name_here/wordpress/' /srv/www/wordpress/wp-config.php
sudo -u www-data sed -i 's/username_here/wordpress/' /srv/www/wordpress/wp-config.php
sudo -u www-data sed -i 's/password_here/<your-password>/' /srv/www/wordpress/wp-config.php
Finally, in a terminal session open the configuration file in nano:
sudo -u www-data nano /srv/www/wordpress/wp-config.php
Find the following:
define( 'AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'NONCE_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'NONCE_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
Delete those lines (ctrl+k will delete a line each time you press the sequence). Then replace with the content of https://api.wordpress.org/secret-key/1.1/salt/. (This address is a randomiser that returns completely random keys each time it is opened.) This step is important to ensure that your site is not vulnerable to “known secrets” attacks.
Save and close the configuration file by typing ctrl+x followed by y then enter
Configure WordPress
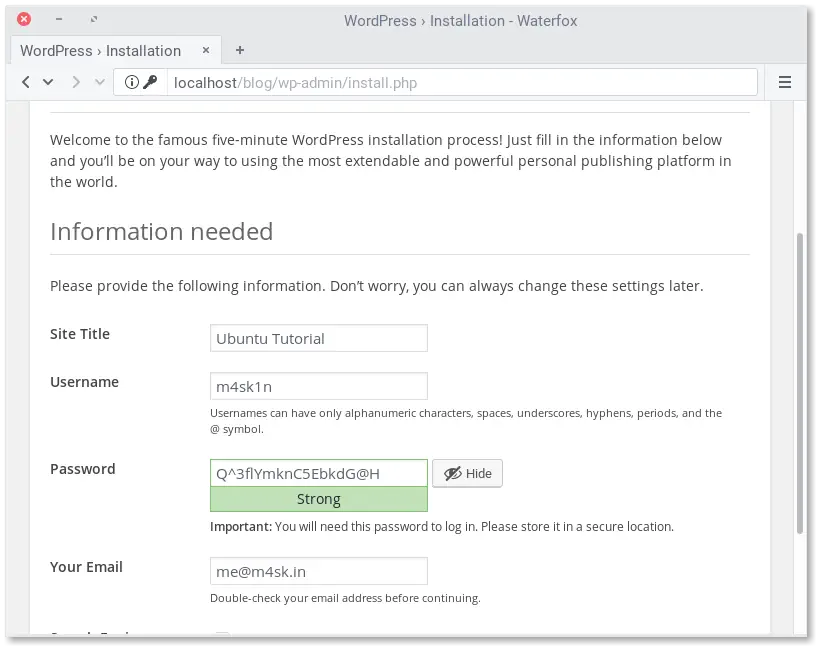
Open http://localhost/ in your browser. You will be asked for title of your new site, username, password, and address e-mail. Note that the username and password you choose here are for WordPress, and do not provide access to any other part of your server – choose a username and password that are different to your MySQL (database) credentials, that we configured for WordPress’ use, and different to your credentials for logging into your computer or server’s desktop or shell. You can choose if you want to make your site indexed by search engines.
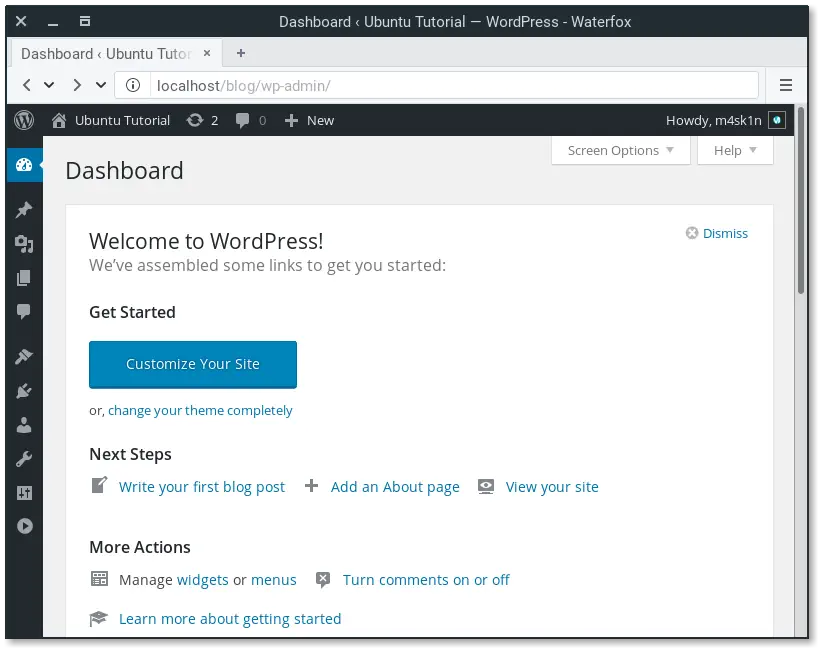
You can now login under http://localhost/wp-login.php. In the WordPress Dashboard, you will see bunch of icons and options. Don’t worry, it’s easy!